
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review
- Basic Research
- Multiple Roles of Sirtuin 6 in Adipose Tissue Inflammation
- Eun Ju Bae, Byung-Hyun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):164-172. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0270
- 3,798 View
- 230 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
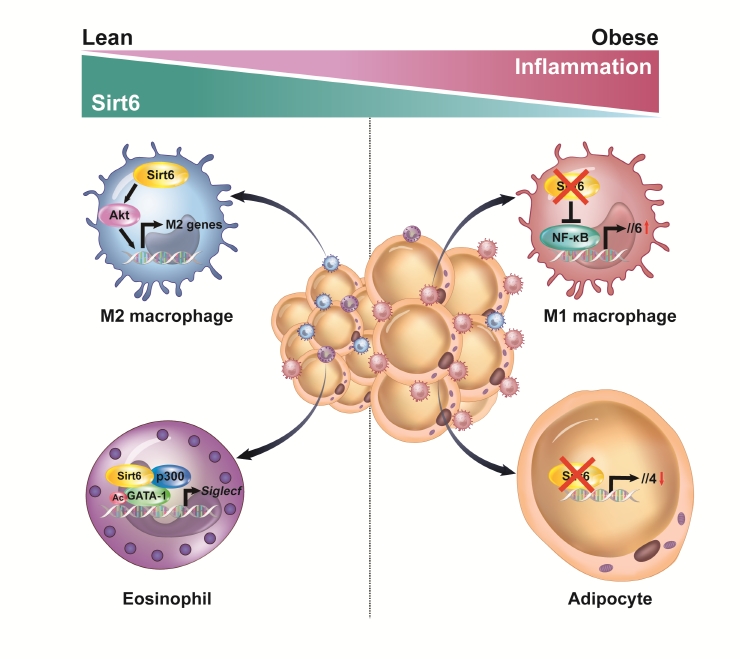
ePub - Adipose tissue (AT) inflammation is strongly associated with obesity-induced insulin resistance. When subjected to metabolic stress, adipocytes become inflamed and secrete a plethora of cytokines and chemokines, which recruit circulating immune cells to AT. Although sirtuin 6 (Sirt6) is known to control genomic stabilization, aging, and cellular metabolism, it is now understood to also play a pivotal role in the regulation of AT inflammation. Sirt6 protein levels are reduced in the AT of obese humans and animals and increased by weight loss. In this review, we summarize the potential mechanism of AT inflammation caused by impaired action of Sirt6 from the immune cells’ point of view. We first describe the properties and functions of immune cells in obese AT, with an emphasis on discrete macrophage subpopulations which are central to AT inflammation. We then highlight data that links Sirt6 to functional phenotypes of AT inflammation. Importantly, we discuss in detail the effects of Sirt6 deficiency in adipocytes, macrophages, and eosinophils on insulin resistance or AT browning. In our closing perspectives, we discuss emerging issues in this field that require further investigation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Increased Expression of Sirtuin 6 in the Prevention of Premature Aging Pathomechanisms
Adrianna Dzidek, Olga Czerwińska-Ledwig, Małgorzata Żychowska, Wanda Pilch, Anna Piotrowska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(11): 9655. CrossRef - Exploring the Influence of Age, Gender and Body Mass Index on Colorectal Cancer Location
Dorel Popovici, Cristian Stanisav, Sorin Saftescu, Serban Negru, Radu Dragomir, Daniel Ciurescu, Razvan Diaconescu
Medicina.2023; 59(8): 1399. CrossRef
- The Role of Increased Expression of Sirtuin 6 in the Prevention of Premature Aging Pathomechanisms
Original Article
- Analgesic Effects of DA-5018, a New Capsaicin Derivative, in Hyperalgesia of Experimental Diabetic Neuropathy.
- Eun Ju Bae, Soon How Kim, Moon Ho Son, Hee Kee Kim, Myeong Soo Shin, Hyun Ji Kim, Won Bae Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 1997;21(1):91-101. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,053 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Painful peripheral neuropathy is one of the most common complications of diabetes and not responsive to conventional analgesics. Capsaicin cream has been used to treat the pain associated with diabetic neuropathy, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and postherpetic neuralgia. But its common side effect, burning sensation, limits the use of it. DA-5018 is a newly synthesized capsaicin derivative which shows more potent systemic and topical analgesia than capsaicin in various animal models of acute and chronic pain, but has little skin irritaion. This study was designed to evaluate the effect of DA-5018 administered systemically or topically on hyperalgesia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic and galactosaemic rats. METHODS: One group of SD rats was treated with streptozotocin(60mg/kg, I.v.) and the pain thresholds were determined weekly by Randall-Selitto paw pressure test. And the other group of SD rats was maintained on 50%-galactose diet until 4~5 weeks and the pain thresholds were determined as well, Drugs were administered subcutaneously once a day for 7 days or topically to the paw for 5 hours a day for 10 days at a time when the hyperalgesia was already present. The increase of pain thresholds by drug was regarded as an indication of analgesia. RESULTS: Streptozotocin-diabetic rats displayed a reduction of pain threshold. Similarly, galactosefeeding resulted in significant reduction of pain threshold. It is concluded that hyperalgesia is a constant feature of sensory dysfunction in experimental models of diabetic and nutritional neuropathy. DA-5018(0.2, 0.5mg/kg, s.c.) produced significant antinociception with efficacy similar to that of capsaicin(10mg/kg, s.c.) in streptozotocin-induced hyperalgesia and furthermore, no tolerance developed for 7 days. And this analgesic effect was superior to desipramine(10mg/kg, s.c.). But ketoprofen(10mg/kg, s.c.) produced no analgesia. Topically, 0.3% DA-5018 cream was as effective as Zostrix-HP(capsaicin 0.075%) both in streptozotocin-diabetic and galactosefed rats while Kenofen gel(ketoprofen 3%) was ineffective to reduce pain. CONCLUSION: These results demonstrate the potent analgesic efficacy of DA-5018 in diabetic pain models and suggest that topical DA-5018 cream may relieves pain caused by diabetic neuropathy offering an alternative for patients not responsive to other treatments or unable to tolerate capsaicin.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





